新加坡政府中学三/四年级数学大纲

新加坡剑桥O水准考试(Singapore-Cambridge General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level Examinations,简称GCE ‘O’ Level),是由新加坡教育部MOE和新加坡考试与评鉴局SEAB共同主办的国家级统一考试,也是新加坡的中学生在4年中学教育结束后参加的考试。
考试一年举办一次,考生可以用获得的成绩为标准申请进入新加坡初级学院、理工学院或工艺教育学院。考试成绩也为英联邦各个国家所承认和接受,可用于申请海外英联邦国家的初级学院或是大学预备班。
贯穿新加坡中学四年教育的,仍是3+1的教学体系,三大模块数学知识和贯穿始终的数学过程思维训练,如下图所示。

数学过程思维这一环节最为关键的是思维技巧和策略思维方法。这部分内容是要求学生在掌握数学知识点的基础上,能活学活用,经过训练,学会常用的思维方法。
新加坡中学三、四年级的知识点如下。
由于新加坡中学四年级即将参加O水准考试,课业多为深度扩展,范围上和中学三年级相当。
一、代数部分
N1. Numbers& operations 数和运算
1.8. use of standard form Ax10n , where n is an integer, and 1 ≤ A ≤ 10
1.9. positive, negative, zero and fractional indices
1.10. laws of indices
N6. Functions & graphs 函数和图
6.8. sketching the graphs of quadratic functions given in the form:
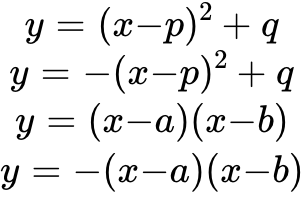
6.9. graphs of power functions = , where n = -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, and simple sums of not more thanthree of these
6.10. graphs of exponential functions = , where is a positive integer
6.11. estimation of the gradient of a curve by drawing a tangent
N7. Equations & inequalities 等式和不等式
7.11. solving quadratic equations in one variable by:
use of formula
completing the square for y = y = x2 + px+q
graphical method
7.12. solving fractional equations that can be reduced to quadratic equations
7.13. solving linear inequalities in one variable (including simultaneous inequalities) and representing the solution on the number line
7.14. formulating a quadratic equation in one variable to solve problems
N8. Set language and notation 集合
8.1. use of set language and the following notation:
Union of A and B ∪
Intersection of A and B ∩
Number of elements in set A ()
“... is an element of ...” ∈
“... is not an element of ...” ∉
Complement of set A ′
The empty set ∅
Universal set ξ
A is a subset of B ⊆
A is a not a subset of B ⊈
A is a (proper) subset of B ⊂
A is a not a (proper) subset of B ⊄
8.2. union and intersection of two sets
8.3. Venn diagrams
N9. Matrices 矩阵
9.1. display of information in the form of a matrix of any order
9.2. interpreting the data in a given matrix
9.3. product of a scalar quantity and a matrix
9.4. problems involving addition, subtraction and multiplication of matrices
二、几何和测量
G2. Congruence & similarity 全等和相似
2.6. scale drawings
2.7. properties and construction of perpendicular bisectors of line segments and angle bisectors
2.8. determining whether two triangles are:
congruent
similar
2.9. ratio of areas of similar plane figures
2.10. ratio of volumes of similar solids
G3. Properties of circles 圆的性质
3.1. symmetry properties of circles:
equal chords are equidistant from the centre
the perpendicular bisector of a chord passes through the centre
tangents from an external point are equal in length
the line joining an external point to the centre of the circle bisects the angle between the tangents
3.2. angle properties of circles:
angle in a semicircle is a right angle
angle between tangent and radius of a circle is a right angle
angle at the centre is twice the angle at the circumference
angles in the same segment are equal
angles in opposite segments are supplementary
G4. Pythagoras’ theorem and trigonometry 三角函数
4.4. extending sine and cosine to obtuse angles
4.5. use of the formula 1/2absinC for the area of a triangle
4.6. use of sine rule and cosine rule for any triangle
4.7. problems in two and three dimensions including those involving angles of elevation and depression and bearings
G5. Mensuration
5.7. arc length, sector area and area of a segment of a circle
5.8. use of radian measure of angle (including conversion between radians and degrees)
G6. Coordinate Geometry 平面几何
6.1. finding the gradient of a straight line given the coordinates of two points on it
6.2. finding the length of a line segment given the coordinates of its end points
6.3. interpreting and finding the equation of a straight line graph in the form y= mx + c
6.4. geometric problems involving the use of coordinates
G7. Vectors in two dimensions 二维空间向量
7.1. use of notations
7.2. representing a vector as a directed line segment
7.3. translation by a vector
7.4. position vectors
7.5. magnitude of a vector
7.6. use of sum and difference of two vectors to express given vectors in terms of two coplanar vectors
7.7. multiplication of a vector by a scalar
7.8. geometric problems involving the use of vectors
三、统计和概率
S1. Data handling & analysis 数据处理和分析
1.11. quartiles and percentiles
1.12. range, interquartile range and standard deviation as measures of spread for a set of data
1.13. analysis and interpretation of:
cumulative frequency diagrams
box-and-whisker plots
1.14. purposes and uses, advantages and disadvantages of the different forms of statistical representations
1.15. calculation of the standard deviation for a set of data (grouped and ungrouped)
1.16. using the mean and standard deviation to compare two sets of data
S2. 概率
2.3. probability of simple combined events (including using possibility diagrams and tree diagrams,where appropriate)
2.4. addition and multiplication of probabilities(mutually exclusive events and independent events)
【注】部分知识点编号并不是从1开始,原因是,每学年都有部分内容是复习上学年的内容,在上学年基础上深入学习,所以相同部分省略,请缺失的编号内容请参考上一学年大纲。






















评论